Strategies for Safe COVID-19 Vaccination
(see Table 1)
- Storage: Be ready to respond to temperature excursions (e.g., refrigerator failure) to prevent wastage.
- Preparation: Provide a quick-reference sheet at the point of dose preparation, and label all
prefilled syringes. - Administration: Use a checklist to identify vaccine contraindications or precautions.
- Documentation: Provide patients with documentation of vaccination. MyMedRec and CanImmunize apps are options to store this information.
INTRODUCTION
This bulletin shares a number of leading practices that facilitate the safe administration of a COVID-19
vaccine. These practices, which incorporate learning from past vaccine errors, will evolve over time, as
additional knowledge is gained and new guidance is developed.
In Canada, as of Feb. 25, 2021, Health Canada has approved 2 COVID-19 vaccines (known by the
names of their manufacturers: Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech), both of which use mRNA technology.1,2 Several vaccines using different technology (e.g., viral vector) are under consideration
for approval.
LEARNING FROM VACCINE ERRORS
Two groups of vaccine errors were reviewed for this bulletin: worldwide incidents reported thus far
involving COVID-19 vaccines and errors that have occurred in Canada with other vaccines. The latter
were identified from a multi-incident analysis3 of more than 1300 vaccine errors reported to 3 ISMP
Canada databases and CIHI’s National System for Incident Reporting database through December
2020.4 The risks and learning are categorized by 4 medication-use stages below and summarized
in Table 1.
Storage

Each COVID-19 vaccine has distinct storage requirements, and all vaccines approved so far require storage in a refrigerator, a freezer, or an ultra-low-temperature freezer. An interruption in the cold chain could result in product spoilage. For example, several incidents have been traced to inadequate equipment for monitoring the temperature of freezers and refrigerators and/or the lack of a plan to deal with temperature excursions.5 To limit potential wastage of vaccine, process checks must be in place to ensure that public health guidance, as well as manufacturers’ temperature storage requirements, is followed.
Vaccine storage, whether in a refrigerator or a freezer, must be carefully scrutinized to ensure that products are appropriately segregated. Errors involving selection of the wrong product have occurred when refrigerators were poorly organized. For example, there have been instances when insulin or a neuromuscular blocker or another vaccine was administered instead of the intended vaccine product.6,7 In all of these incidents, a key contributing factor was storage of multiple products in close proximity. Ideally, bar-coding will be used during the vaccine selection step, as well as during preparation and administration.
The Pfizer-BioNTech product requires dilution after thawing, but the diluent is not supplied with the product and must be sourced separately.1 Inoculation of undiluted vaccine has been reported. Bundling the diluent vial with the vaccine vial when the latter is removed from the freezer provides workflow support to help prevent errors.
Preparation
Develop a standardized process for preparing doses8 and provide a quick-reference sheet at the point of dose preparation. Errors related to vaccine preparation include withdrawal and administration of the contents of an entire multidose vial to a single patient, needle-syringe misconnection, preparation of an incorrect volume, as well as inadequate or no dilution and administration of diluent only.9-14 To prevent preparation errors, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) has developed a COVID-19 Vaccine Handling Toolkit highlighting a number of operational considerations.15
As part of the standardized process, labelling of prefilled syringes is essential, because it provides an
opportunity for an extra check before dose administration. The syringe label should specify the name of the product (and its manufacturer), the dose (volume) for injection, the lot number, and the beyond-use date and time (i.e., the last date and time of day when the product can be used). It is also important to label any opened, partially used vials with both the puncture and beyond-use dates and times.
Administration
The person administering the vaccine should be alert to visual cues indicating a potential undetected error from a previous step (e.g., appearance of syringe contents differing from expectations, incorrect volume). Injection of an incorrect volume for multiple patients has been reported.14 Review of a labelled syringe prior to administration supports the identification of a potential error.
Before administration of a COVID-19 vaccine, each patient should be screened for contraindications or reasons that would affect their suitability for vaccination. For example, current guidelines advise
separating administration of the COVID-19 vaccine by 14-28 days from most other vaccine products
(e.g., shingles vaccine).16 If possible, the timing of future inoculations with a COVID-19 and other
planned vaccines needs to be considered.
Shoulder injury related to vaccine administration, also known as SIRVA, is a well-established
preventable adverse effect resulting from improper landmarking technique (Figure 1).17 It is easier for those administering the vaccine to identify the correct injection site if the patient’s upper arm is bare. Accordingly, patients should be advised to wear suitable clothing (i.e., sleeveless/short-sleeved tops) to their appointment. In addition, vaccine stations should be set up to allow privacy.
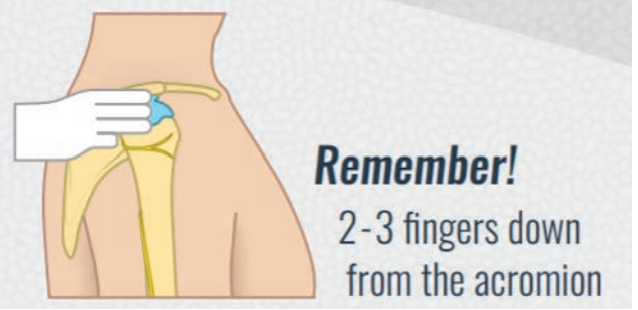
FIGURE 1: Landmarking poster to prevent SIRVA. Reproduced with permission of University of Waterloo School of Pharmacy ©Pharmacy5in5.com.
Documentation
The currently available COVID-19 vaccines require 2 doses for maximum efficacy; there is a risk that the wrong product could be used for the second dose. At the time of publication, the National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI) is recommending that the vaccine series for each
person be completed with the same COVID-19 vaccine; however, NACI also acknowledges that if
the same product is not available at the time of the second dose, a vaccine of similar type (e.g., another mRNA product, if the first dose was an mRNA product) can be used.16

Providing patients with documentation of vaccination can prevent errors. When patients presenting for their second dose do not know which product they received initially, such documentation can be used to confirm or identify the correct vaccine to be administered. Patients can also be encouraged to take a picture of the documentation or to enter it into a medication app such as MyMedRec or CanImmunize.
Documentation also supports the prevention of scheduling errors. Each of the currently approved
vaccines has its own recommended interval between the 2 required doses. Information about the
COVID-19 vaccines provided by Health Canada and NACI16 includes information about the timing
of COVID-19 vaccine doses, as well as the timing of these doses in relation to administration of other
vaccine products.
Booking a patient’s second appointment at the time of the first visit will support vaccination at
the right time, when possible. There has been a report describing a scheduling error due to
miscommunication.13 Follow-up by phone, text, or email is recommended to ensure patients receive
the second dose on time.18
CONCLUSION
Knowledge about the appropriate use and safety of COVID-19 vaccines will continue to evolve, and
guidance from health authorities, such as Health Canada, NACI, public health organizations, and
provincial/territorial health ministries, will be updated regularly.
Vaccine-related adverse drug reactions should be reported through the customary reporting channels.
In addition, consider documenting vaccine errors (regardless of outcome) through an organization’s
usual reporting process and/or ISMP Canada’s Individual Practitioner Reporting program. These
reports will support future learning and error prevention.
TABLE 1: Strategies for Safe Immunization with COVID-19 Vaccines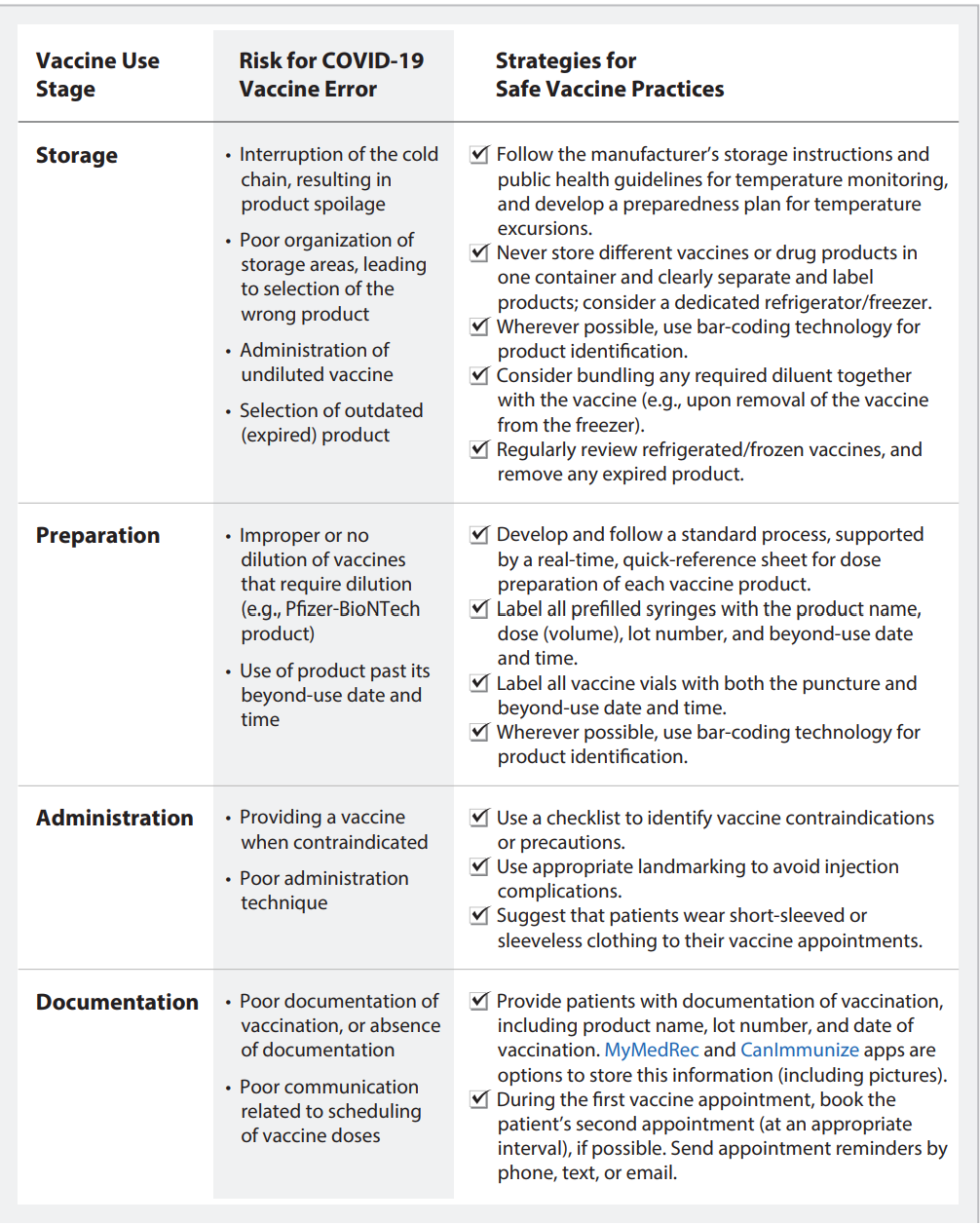
REFERENCES
- Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine [product monograph]. Mainz (DE): BioNTech Manufacturing GmbH; 2020 Dec 9 [cited 2021 Feb 2]. Available from: https://www.pfizer.ca/sites/default/files/202012/Pfizer-BioNTech_COVID-19_Vaccine_PM_EN_244906_09Dec2020.pdf
- Moderna COVID-19 vaccine [product monograph]. Cambridge (MA): Moderna Therapeutics Inc; 2020 Dec 23 [cited 2021 Feb 2]. Available from: https://covid-vaccine.canada.ca/info/pdf/moderna-covid-19-vaccine-pm1.pdf
- Injecting standardization into vaccine clinics. ISMP Can Saf Bull. 2018 [cited 2021 Feb 2];18(7):1-4. Available from: https://www.ismp-canada.org/download/safetyBulletins/2018/ISMPCSB2018-i7-VaccineClinics.pdf
- National System for Incident Reporting. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Institute for Health Information. 2020 [cited 2020 Nov 29]. Available from: https://www.cihi.ca/en/national-system-for-incident-reporting-nsir
- Wyland S. Storage problem causes loss of 75 vaccine doses in New Mexico. Sante Fe New Mexican. 2020 Dec 15 [updated 2020 Dec 16; cited 2021 Feb 2]. Available from:
https://www.santafenewmexican.com/news/coronavirus/storage-problem-causes-loss-of-75-vaccine-doses-in-new-mexico/article_4e70b3f8-3f36-11eb-aa6d-67224f55fb2b.html - Wray M. 10 people hospitalized after getting insulin instead of flu shot. Global News. 2019 Nov 8 [cited 2020 Feb 17]. Available from: https://globalnews.ca/news/6144753/insulin-flu-shot/
- Grissinger M. Paralyzed by mistakes – reassess the safety of neuromuscular blockers in your facility. PT 2019;44(3):91-93,107. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6385733/
- Model standards for pharmacy compounding of non-hazardous sterile preparations. Ottawa (ON): National Association of Pharmacy Regulatory Agencies; 2016 [cited 2021 Feb 3]. Available from: https://napra.ca/general-practice-resources/model-standards-pharmacy-compounding-non-hazardous-sterile-preparations
- Magder J. One of first COVID-19 vaccinations in Canada appears to have been botched. Montreal Gazette. 2020 Dec 18 [cited 2021 Feb 2]. Available from: https://montrealgazette.com/news/local-news/nurse-appears-to-have-botched-one-of-first-covid-19-vaccines-in-canada
- Staff T. Pharmacist accidentally injected with 4 COVID vaccine doses. Times Israel. 2020 Dec 22 [cited 2021 Feb 2]. Available from: https://www.timesofisrael.com/pharmacist-accidentally-injected-with-4-covid-vaccine-doses/
- Medical professional received 5 to 6 doses of COVID vaccine in one shot. Jerusalem Post. 2020 Dec 22; [cited 2021 Feb 2]. Available from: https://www.jpost.com/israel-news/medical-professional-received-5-6-doses-of-covid-vaccine-in-one-shot-652871
- Coronavirus: German care home workers accidentally given vaccine overdose. Deutsche Welle. 2020 Dec 28 [cited 2021 Feb 2]. Available from: https://www.dw.com/en/coronavirus-german-care-home-workers-accidentally-given-vaccine-overdose/a-56077717
- Learning from errors with the new COVID-19 vaccines. Horsham (PA): Institute for Safe Medication Practices; 2021 Jan 14 [cited 2021 Feb 11]. Available from: https://www.ismp.org/resources/learning-errors-new-covid-19-vaccines
- Patients receive wrong dosage of COVID-19 vaccine at Massachusetts CVS pharmacy. WCBV Boston. 2021 Feb 17 [cited 2021 Feb 17]. Available from: https://www.wcvb.com/article/wrong-dosage-of-covid-19-vaccine-ipswich-massachusetts-cvs-pharmacy/35542670
- COVID-19 vaccine handling toolkit: Operational considerations for healthcare practitioners [version 2.0]. Rockville (MD): The United States Pharmacopeial Convention; 2021 Jan [cited 2021 Feb 8]. Available from: https://www.usp.org/covid-19/vaccine-handling-toolkit
- Vaccine administration. In: Recommendations on the use of COVID-19 vaccines. Ottawa (ON): Health Canada; 2021 Jan 12 [cited Feb 2]. Available from: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/immunization/national-advisory-committee-on-immunization-naci/recommendations-use-covid-19-vaccines.html#b4
- Bancsi A, Houle SKD, Grindrod KA. Getting it in the right spot: shoulder injury related to vaccine administration (SIRVA) and other injection site events. Can Pharm J. 2018;151(5):295-299.
- Gavin K. How to make sure people get the second dose of the COVID-19 vaccine. Ann Arbor (MI): M Health Lab; 2020 Dec 14 [cited 2021 Feb 2]. Available from: https://labblog.uofmhealth.org/rounds/how-to-make-sure-people-get-second-dose-of-covid-19-vaccine
